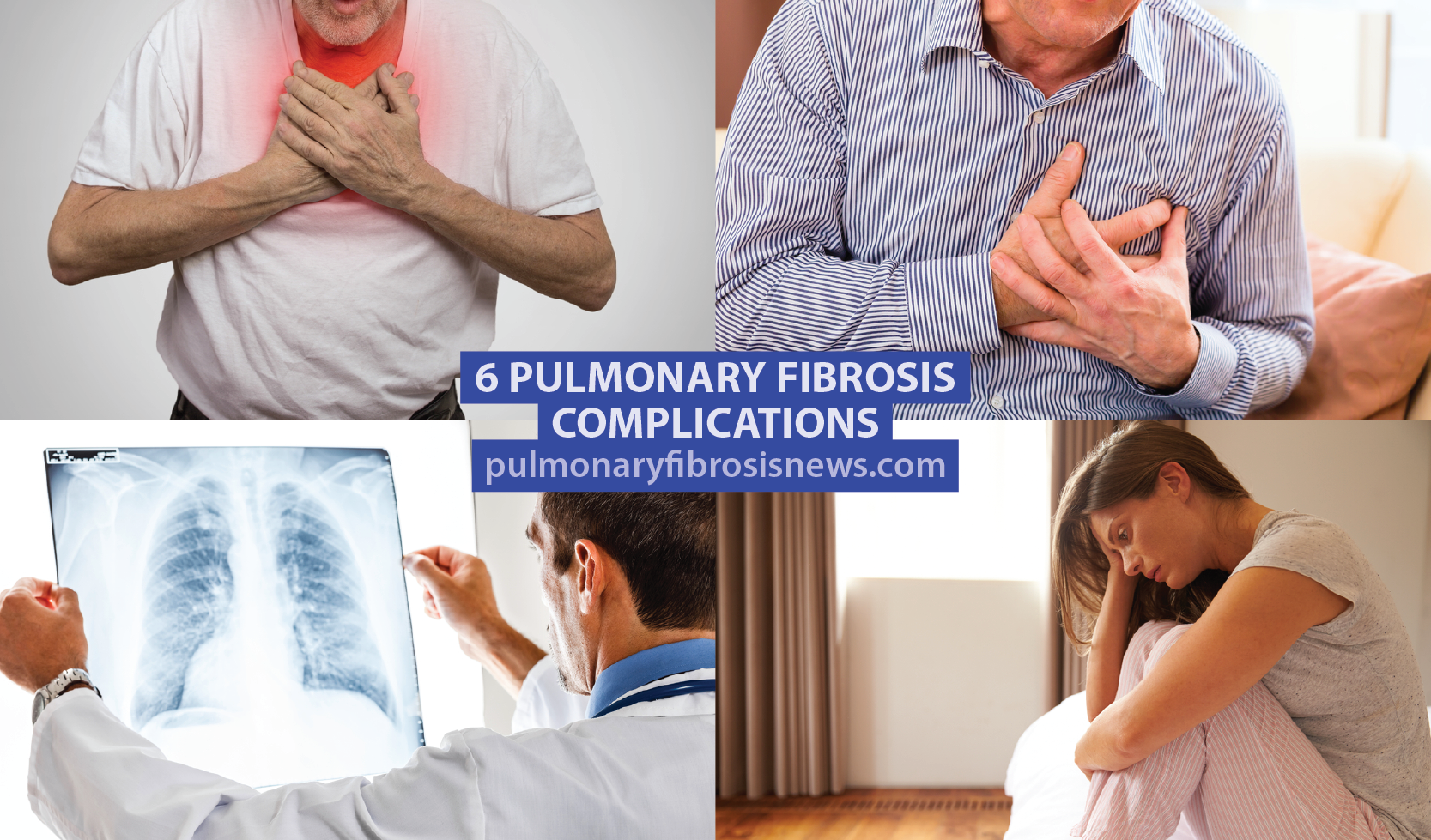
6 Pulmonary Fibrosis Complications
Written by |
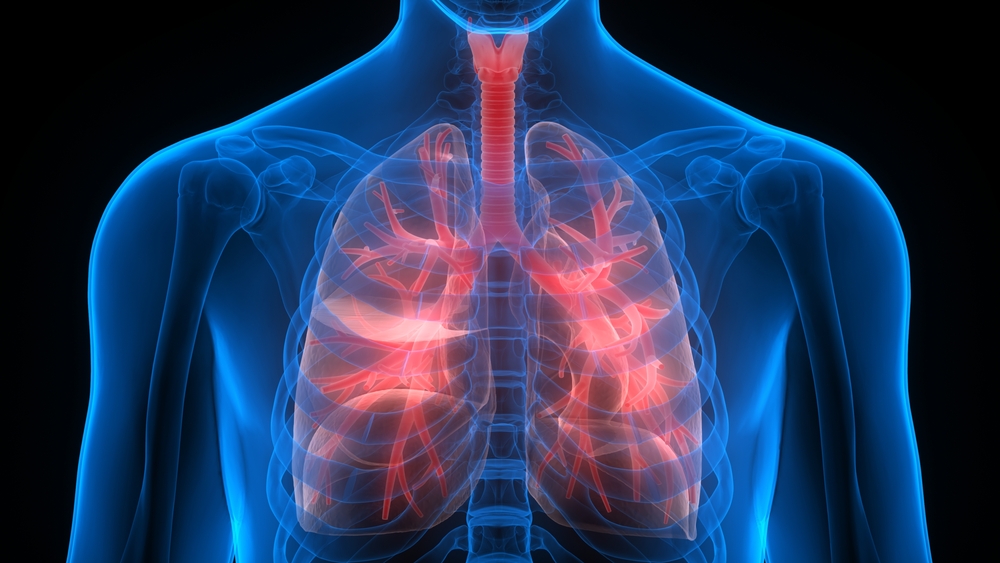
According to the Mayo Clinic, though no current cure for pulmonary fibrosis exists yet, medications and other treatment options can help improve a patient’s quality of life.
As the disease evolves, several complications may arise. Here is a list of six possible pulmonary fibrosis complications:
1. High blood pressure in the lungs: Unlike normal high blood pressure, this condition is different because it only affects your lung’s arteries. It begins when the smallest arteries and capillaries are compressed by scar tissue, causing increased resistance to blood flow in your lungs. This creates pressure within the pulmonary arteries and the right ventricle, and can result in the development of pulmonary hypertension.
Here are 4 things you can do to help prevent pulmonary fibrosis.
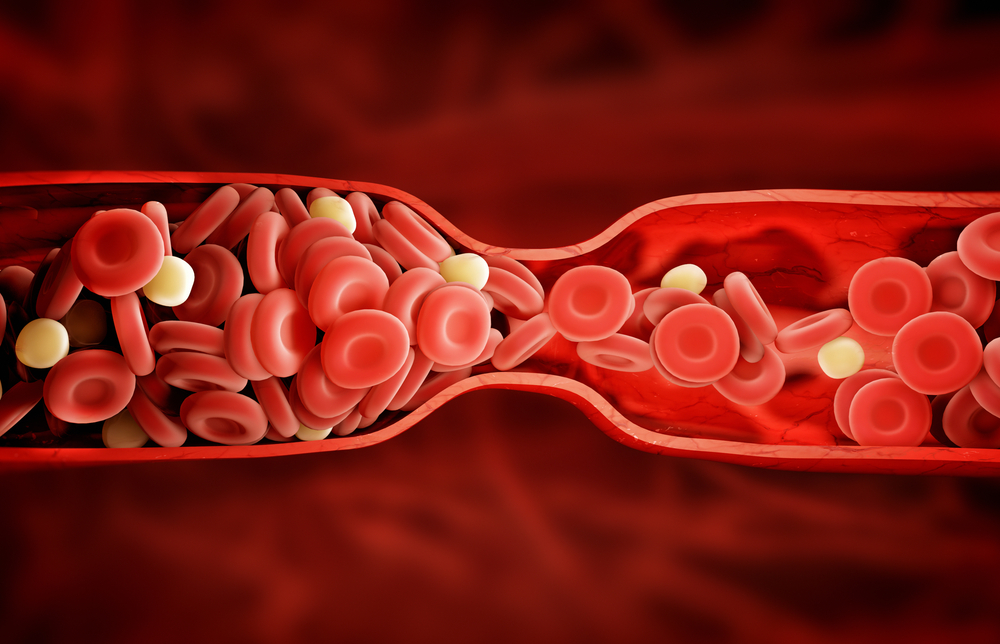
2. Blood clots: Sluggish blood flow increases the risk of developing blood clots.
How can you better manage your pulmonary fibrosis? Find out here.

3. Right-sided heart failure: This can occur when the lower right ventricle of your heart has to pump harder than usual to move blood through partially blocked pulmonary arteries.
Learn some simple facts about pulmonary fibrosis.
4. Respiratory failure: Respiratory failure is a serious and devastating reality. Although it often occurs in the last stage of the disease, respiratory failure happens when blood oxygen levels fall dangerously low.
Here are 4 things you can do to help prevent pulmonary fibrosis.
5. Lung cancer: Chronic lung diseases like pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary fibrosis can increase the risk of other lung disease.
How can you better manage your pulmonary fibrosis? Find out here.

6. Depression: Depression can develop with any chronic and life threatening disease. Because pulmonary fibrosis is serious and frightening, it is quite normal for many patients to struggle with depression.
Learn a few more facts about pulmonary fibrosis.
Pulmonary Fibrosis News is strictly a news and information website about the disease. It does not provide medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. This content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.